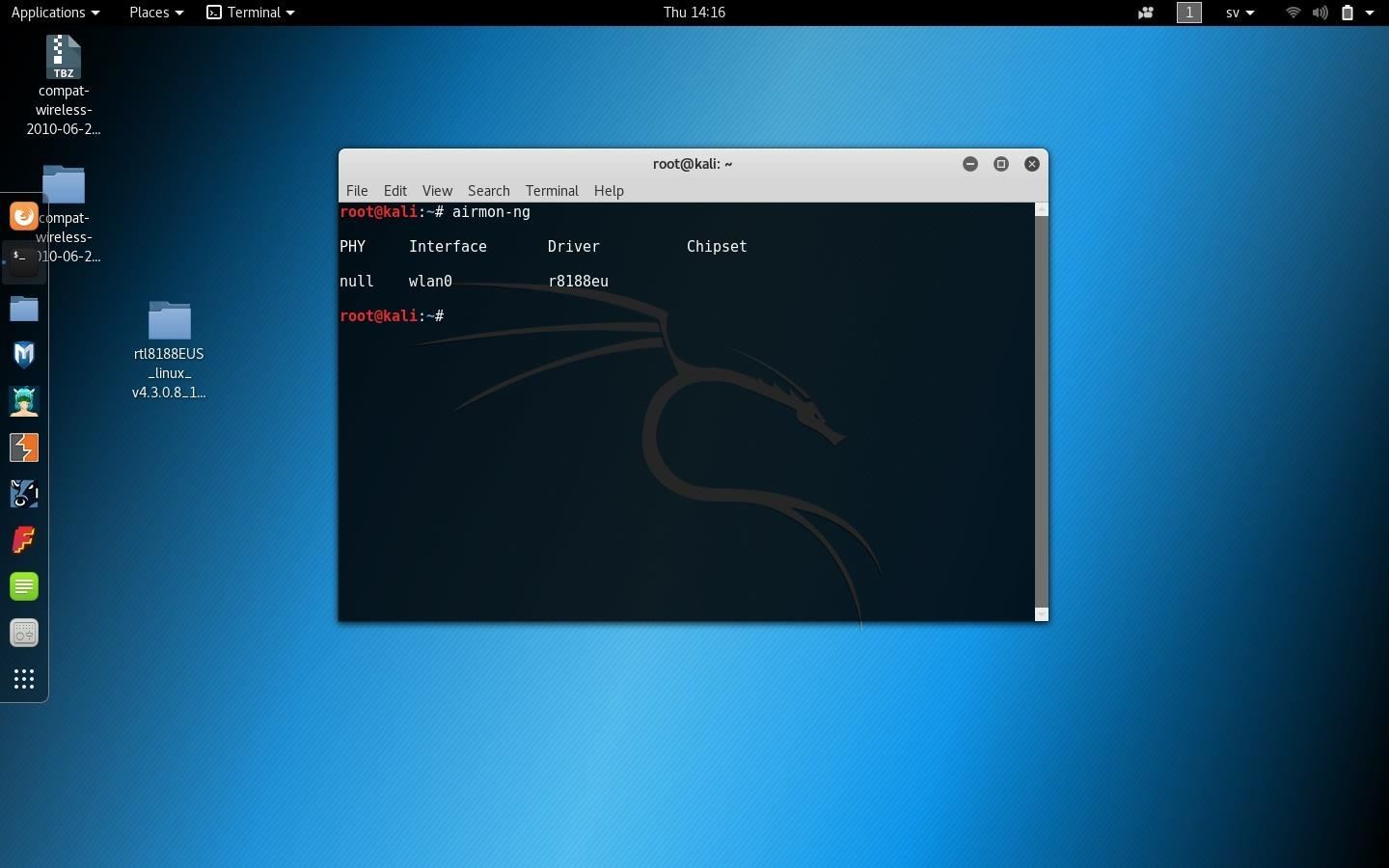
Open Interface Network & Wireless Cards Driver
The Benefits of Working on an Open Source 5G Network. Users can expect to see greater network improvements in a shorter time frame thanks to open source software and open interface hardware. There are a variety of benefits and features that DISH Wireless is bringing customers. Let’s begin with where we left off, network slicing. Sometimes, though, you’ll want to allow otherwise restricted traffic through your firewall. To do so, you’ll have to open a port. When a device connects to another device on a network (including the internet), it specifies a port number that lets the receiving device know how to handle the traffic. CANopen is a communication protocol and device profile specification for embedded systems used in automation. In terms of the OSI model, CANopen implements the layers above and including the network layer. The CANopen standard consists of an addressing scheme, several small communication protocols and an application layer defined by a device profile. The communication protocols have support for network management, device monitoring and communication between nodes, including a simple transport la. Method 1: Open Network Connections via Run or Command Prompt. Press the Windows key and the R key at the same time to open the Run box. Type ncpa.cpl and hit Enter and you can access Network Connections immediately. A similar way of opening Network Connections is to run ncpa.cpl at the Command Prompt. Method 2: Open Network Connections via Taskbar.
Try these things to troubleshoot network connection issues in Windows 10.
Use the Network troubleshooter. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Under Change your network settings, select Network troubleshooter. Open Status settings
Make sure Wi-Fi is on. Select Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi. Next, select Show available networks, and if a network you expect to see appears in the list, select it, then select Connect. Open Wi-Fi settings
See if you can use the Wi-Fi to get to websites from a different device. If you can’t, restart your modem, router, and device, and re-connect to the Wi-Fi.
If your Surface still isn't connecting, try the steps on Surface can't find my wireless network.
Which is the right network interface to capture from?
Contents

- Network Interfaces
- Interface names
- Troubleshooting
'Capture/Interfaces' dialog
The 'Capture/Interfaces' dialog provides a good overview about all available interfaces to capture from.
If you are unsure which interface to choose this dialog is a good starting point, as it also includes the number of packets currently rushing in.
Interface preferences
In the Wireshark preferences (Edit/Preferences/Capture), you can:
- add a descriptive name to an interface
- even completely hide an interface from the capture dialogs
See Preferences/Capture for details.
Interface names
Adi network & wireless cards driver. There are some common interface names which are depending on the platform.
Windows
The interfaces names are provided by the network card manufacturer, which can be helpful to identify an interface.
WinPcap provides some special interface names:
'Generic dialup adapter': this the name of the dialup interface (usually a telephone modem), see CaptureSetup/PPP
'Generic NdisWan adapter': old name of 'Generic dialup adapter', please update Wireshark/WinPcap!
Wireless interfaces can usually be detected with names containing: 'Wireless', 'WLAN', 'Wi-Fi' or '802.11', see CaptureSetup/WLAN for capturing details.
General UNIX/Linux
On most systems you can get a list of interfaces by running 'ifconfig' or 'ifconfig -a'.
Open Interface Network & Wireless Cards Drivers
{Free,Net,Open,Dragonfly}BSD
'lo0': virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback
'ppp0', 'ppp1', etc.: PPP interfaces, see CaptureSetup/PPP
Other names: other types of interfaces, with names that depend on the type of hardware; see the appropriate page under CaptureSetup
Open Interface Network & Wireless Cards Drivers
Linux
- 'any' : virtual interface, captures from all available (even hidden!) interfaces at once
'lo': virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback
'eth0', 'eth1', ..: Ethernet interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet
'ppp0', 'ppp1', ..: PPP interfaces, see CaptureSetup/PPP
'wlan0', 'wlan1', ..: Wireless LAN, see CaptureSetup/WLAN
- 'team0', 'bond0': Combined interfaces (i.e. NIC teaming or bonding)
'br0', 'br1', ..: Bridged Ethernet, see Ethernet Bridge + netfilter Howto
'tunl0', 'tunl1': IP in IP tunneling, see http://www.linuxguruz.com/iptables/howto/2.4routing-5.html
'gre0', 'gre1': GRE tunneling (Cisco), see http://www.linuxguruz.com/iptables/howto/2.4routing-5.html
- 'ipsec0', 'ipsec1': IPsec (VPN)
'nas0', 'nas1': ATM bridging as in RFC 2684 (used e.g. for xDSL connections), see http://home.regit.org/?page_id=8
'usb0', 'usb1', ..: USB interfaces, see CaptureSetup/USB
macOS
'lo0': virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback
'ppp0', 'ppp1', etc.: PPP interfaces, see CaptureSetup/PPP
'en0', 'en1', ..: Ethernet or AirPort interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet for Ethernet and CaptureSetup/WLAN for AirPort
'fw0', 'fw1', ..: IP-over-FireWire interfaces
Solaris
The lists of Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring interfaces are not necessarily complete; please add any interfaces not listed here. Also, list other interfaces supported.
beN, bgeN, ceN, dmfeN, dnetN, e1000gN, eeproN, elxlN, eriN, geN, hmeN, ieeN, ieefN, iprbN, ixgbN, leN, neeN, neiN, nfeN, pcelxN, pcnN, peN, qeN, qfeN, rtlsN, sk98solN, smcN, smceN, smceuN, smcfN, spwrN, xgeN: Ethernet interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet
sxpN: FDDI interfaces
trN: Token Ring interfaces, see CaptureSetup/TokenRing
fcipN: IP-over-Fibre Channel interfaces
ibdN: IP-over-Infiniband interfaces (not currently supported by libpcap, hence not currently supported by Wireshark)
idnN: inter-domain virtual interfaces
baN: raw ATM interfaces
HP-UX
lanN: Ethernet, FDDI, or Token Ring interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet for Ethernet and see CaptureSetup/TokenRing for Token Ring
AIX
lo0: virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback
enN, etN: Ethernet interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet
fiN: FDDI interfaces
trN: Token Ring interfaces, see CaptureSetup/TokenRing
Digital/Tru64 UNIX
The list of Ethernet interfaces is not necessarily complete; please add any interfaces not listed here. Also, list other interfaces supported.
lo0: virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback Olivetti Laptops & Desktops Driver Download for windows.
pppN: PPP interfaces, see CaptureSetup/PPP
tuN: Ethernet interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet
IRIX
The lists of Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring interfaces are not necessarily complete; please add any interfaces not listed here. Also, list other interfaces supported.
lo0: virtual loopback interface, see CaptureSetup/Loopback
pppN: PPP interfaces, see CaptureSetup/PPP
ecN, efN, egN, epN, etN, fxpN, gfeN, vfeN, tgN, xgN: Ethernet interfaces, see CaptureSetup/Ethernet
elN: ATM LANE emulated Ethernet interfaces
qaaN: ATM 'classical IP' interfaces
faN: FORE ATM interfaces
cipN: ???
ipgN, rnsN, xpiN: FDDI interfaces
mtrN: Token Ring interfaces, see CaptureSetup/TokenRing
qfaN: IP-over-Fibre Channel interfaces
Troubleshooting
Having trouble selecting the right interface?
Required interface not listed (or no interfaces listed at all)
Problem: The network interface you want to capture from isn't in the list of interfaces (or this list is completely empty).
There are several possible causes:

Prerequisites: check the CaptureSetup/CaptureSupport and CaptureSetup/CapturePrivileges pages
WinPcap (Windows only): check the WinPcap page for known limitations and the recommended WinPcap version (esp. for 64bit and Vista)
- Interface hidden: did you simply hide the interface in question in the Edit/Preferences/Capture dialog?
Which interface to choose?
Problem: The capture dialog shows up several network interfaces and you're unsure which one to choose.
You could:
.jpg)
- use the Capture/Interfaces dialog, which shows the number of packets rushing in and may show the IP addresses for the interfaces
- try all interfaces one by one until you see the packets required
- Win32: simply have a look at the interface names and guess
If you're trying to capture traffic between your machine and some other machine, and your machine has multiple network interfaces, at least for IP traffic you can determine the interface to use if you know the IP addresses for the interfaces and the IP address for the first hop of the route between your machine and that other machine.
To determine the IP address for the first hop of the route, use traceroute, if available, on UN*X systems, and tracert on Windows systems.
